When
working with large datasets in Excel, errors are inevitable. Whether it's a
division by zero, missing values, or formula mistakes, errors can disrupt your
calculations and analysis. The Excel IFERROR function is your go-to tool
to handle these issues effectively. In this guide, we’ll cover how to use
IFERROR, its syntax, practical use cases, and why it’s essential for
error-proofing your Excel work.
What is the IFERROR Function?
The
IFERROR function in Excel is designed to catch errors in formulas and
replace them with a value of your choice. Instead of leaving error messages
like #DIV/0!, #N/A, or #VALUE! in your spreadsheet, you can display something
more useful—like a zero, blank cell, or custom message. This function is
particularly useful when you’re dealing with complex formulas or pulling data
from external sources that may have missing or incorrect values.
Syntax of the IFERROR Function
=IFERROR(value,
value_if_error)
- value: The expression or
formula to evaluate.
- value_if_error: What to display if the
formula results in an error.
How Does IFERROR Work?
IFERROR
works by evaluating the expression in the value argument. If that expression
evaluates correctly, Excel will return the result. However, if the expression
returns an error, the function will instead return whatever you specify in the value_if_error
argument.
Practical Examples of Using IFERROR
1. Handling Division by Zero
In
many Excel models, dividing by zero leads to the #DIV/0! error. Instead of
leaving this error visible in your worksheet, you can use IFERROR to manage it.
Example:
=IFERROR(E2/F2,"Error:Division
by zero")
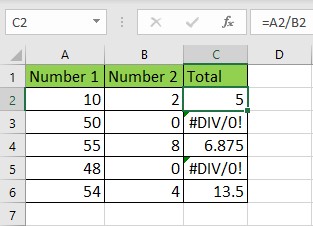
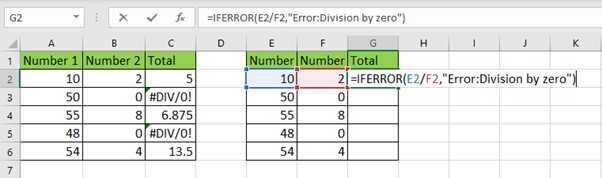
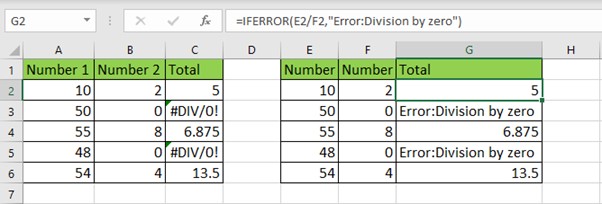
If F2 contains zero, the formula will return "Error: Division by zero" instead of the #DIV/0! message.
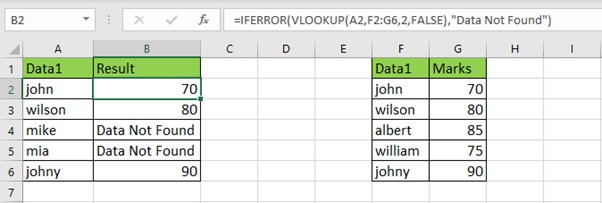
2. Cleansing Data from External Sources
When
you import data from external systems, you might encounter incomplete data,
leading to errors. IFERROR can help by cleaning up the output and providing
more readable results.
Example:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(A2,F2:G6,2,FALSE),"Data
Not Found")
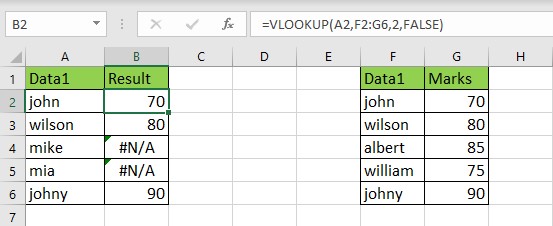
3. Error Handling in Complex Calculations
If
you’re using complex formulas that reference multiple sheets or datasets, an
error at any point can break the entire calculation. IFERROR provides a
safeguard for such scenarios.
Example:
=IFERROR(SUM(A1:A10)/SUM(B1:B10),
"Calculation Error")
This formula will return "Calculation Error" if SUM(B1:B10) equals zero, preventing the #DIV/0! error.
Why Use IFERROR?
1. Improves
Data Presentation:
Replacing errors with meaningful messages makes your data easier to understand.
2. Boosts
Productivity:
Instead of manually checking and fixing errors, IFERROR automates the process.
3. Prevents
Broken Formulas:
In models that use multiple functions and references, IFERROR ensures that a
single error doesn't disrupt the entire calculation.
IFERROR vs. IF Function: What’s the Difference?
You
may wonder if you can handle errors with a simple IF function. While
it’s true that IF can be used to manage certain errors, it’s not as efficient
as IFERROR. With IF, you need to manually set up conditions for each possible error,
which can become cumbersome. On the other hand, IFERROR automatically catches
any error and handles it in one step, making it a more streamlined solution.
Conclusion
The
IFERROR function is an essential tool for anyone working with formulas in
Excel. It not only cleans up your data but also ensures that errors don’t
disrupt your analysis. Whether you’re handling division by zero, incomplete
data, or complex calculations, IFERROR can save you time and headaches.
Comments
Post a Comment